What is A/B Testing of Menu Navigation For Medical Websites?
Why A/B Testing Navigation Matters for Medical Websites: A/B testing of menu navigation on medical websites involves creating two different versions of your website’s navigation menu and presenting each version to a segmented portion of your website’s users. The goal is to collect data on how each version impacts user behavior and ultimately determine which navigation structure performs better in terms of achieving your website’s objectives, such as increased patient engagement, appointment bookings, or information access.
Effective website navigation is critical to ensure that visitors can quickly find the information they need, whether they are looking for services, booking an appointment, or simply learning more about the medical practice. Poor navigation can frustrate users and lead them to leave the site, while an optimized navigation experience can lead to higher engagement and better conversion rates (e.g., appointment bookings, form submissions, phone calls).
A/B testing navigation helps medical websites optimize this experience and ensure that visitors can easily and efficiently find what they need, ultimately leading to higher patient acquisition and satisfaction.
A/B testing (also known as split testing) of navigation is a data-driven method for optimizing a medical website’s menu and structure. In its simplest form, it’s a controlled experiment where you compare two versions of your website’s navigation to see which one performs better at achieving a specific goal.
- Version A (The Control): Your current, existing website navigation.
- Version B (The Variation): A new version with a specific, intentional change.
Website visitors are randomly shown either Version A or Version B. The system then tracks user behavior to see which version leads to more conversions—like more clicks on the “Book Appointment” button or fewer people leaving the site in frustration.
Analogy: Imagine the lobby of your healthcare practice. A/B testing is like having two different sets of directional signs. On Monday, you use Signage Set A. On Tuesday, you use Setage Set B. At the end of the week, you measure which set led to more patients finding the correct department without asking for help. A/B testing does this digitally, simultaneously, and with statistical accuracy.
Why is A/B testing of menu navigation is important for medical websites?
For a medical practice, a website’s navigation is one of its most critical components. A confused or frustrated visitor is a lost patient, especially when they may already be feeling anxious or unwell.
- Reduces Patient Friction and Anxiety: A clear, intuitive navigation system reassures patients and makes them feel confident. A confusing menu can increase stress and cause them to abandon the site for a competitor whose site is easier to use.
- Increases Conversions on Key Goals: The primary goal of a medical website is to get patients to book appointments. If the navigation makes it easier to find the “Book Now” button, the “Find a Doctor” page, or the clinic’s phone number, the conversion rate will increase directly.
- Improves User Experience and SEO: Google’s algorithms favor websites that provide a good user experience. When users can easily navigate your site, they tend to stay longer, view more pages, and have lower bounce rates. These are all positive signals that can improve your search engine rankings over time.
- Accommodates Diverse Patient Demographics: The population in your city and surrounding areas is diverse in age and tech-savviness. A/B testing allows you to find a navigation structure that is clear and simple for all users, not just the ones who are comfortable with complex web interfaces.
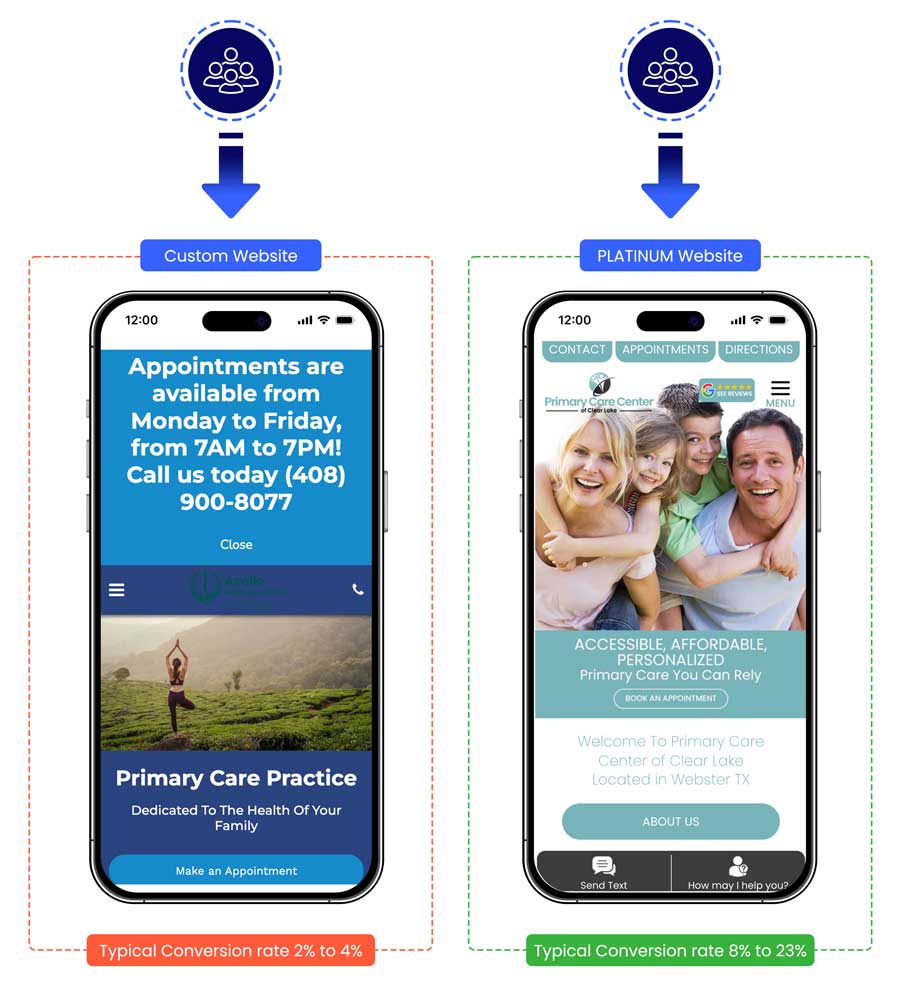
- If you use PatientGain’s PLATINUM service, you get A/B tested website. Which means PLATINUM websites perform much better than randomly created custom websites. Custom websites, almost never go through rigorous A/B testing.